Difference between revisions of "VMS IDE how to"
| Line 357: | Line 357: | ||
# Type “''>vms-ide: Upload all''” in the '''Command Palette''' bar | # Type “''>vms-ide: Upload all''” in the '''Command Palette''' bar | ||
# Select the “''vms-ide: Upload all''” command from the drop-down list | # Select the “''vms-ide: Upload all''” command from the drop-down list | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Building on VMS==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Select the '''Project Explorer''' in the '''Activity''' bar | ||
| + | # Select the project | ||
| + | # Right-click the '''buildName''' in the project description of the Project Explorer, then select '''Change → Select build configuration''' | ||
| + | # Invoke '''“Command Palette”''': press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<nowiki><P></nowiki> | ||
| + | # Type “''>vms-ide: build project''” in the '''Command Palette''' bar | ||
| + | # Select the “''vms-ide: build project''” command from the drop-down list | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Change_build_conf.png|400px|none|none|change build conf]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The project will be built. Info about the build process will be shown in the '''Output''' tab. | ||
[[Category:VMS IDE]] | [[Category:VMS IDE]] | ||
Revision as of 12:02, 13 April 2021
Contents
- 1 Installing Visual Studio Code
- 2 Installing VMS IDE extension
- 3 Creating and setting up a project
- 4 Working on a project
Installing Visual Studio Code
To start working with VMS IDE you need to install Visual Studio Code editor.
- Go to https://code.visualstudio.com/
- Click the download dropdown button and select the build for your platform (Windows, Mac, or Linux). The installer will be downloaded.
- Run the installer and follow the instructions
(!) This guide uses Visual Studio Code for Windows
Installing VMS IDE extension
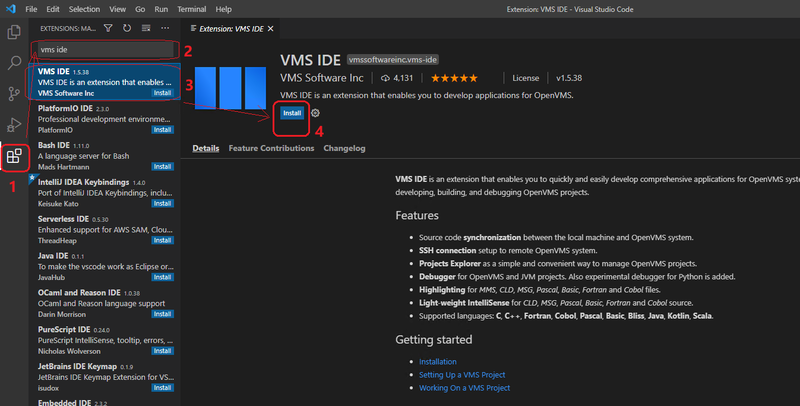
- Select Extensions view in the Activity Bar
- Type “vms ide” into the search box
- Select VMS IDE extension
- Click the Install button in the Extensions view
VS Code will install the extension. To verify that it is installed:
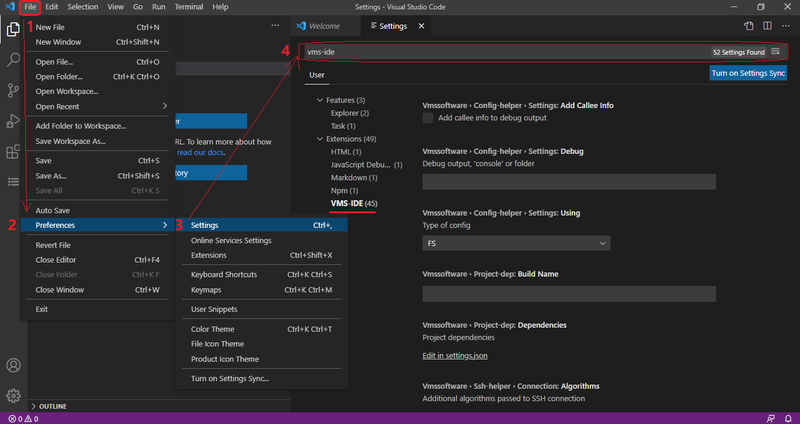
- Go to File → Preferences → Settings
- Type “vms ide” to the Search bar in the Settings tab
The extension will be displayed in the list of settings:
Creating and setting up a project
Creating a project folder
To start working on your project you need to open the folder that will be used as a project folder.
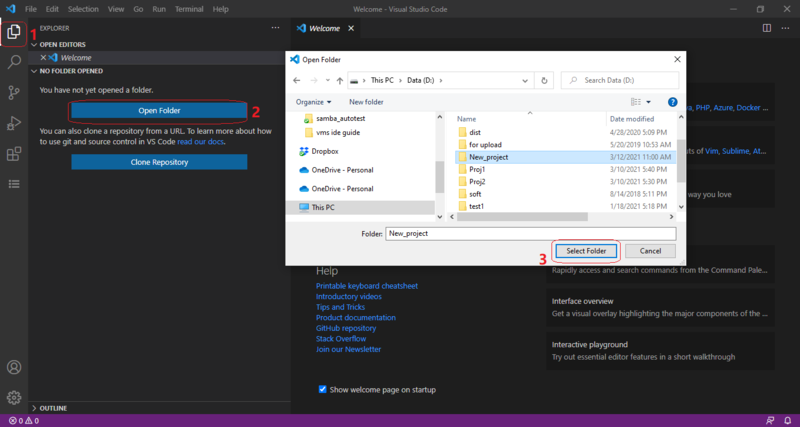
- Select the Explorer view in the Activity bar
- Click the Open Folder button
- Select a folder for the project in the dialog window and click the Select Folder button.
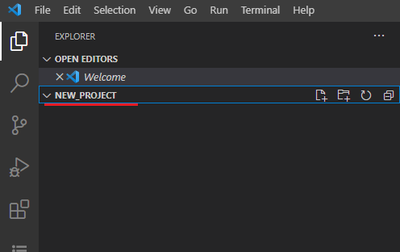
The selected folder is shown in the Explorer tab. All project files and directories will be shown in this panel.
The alternative way to open the folder: File → Open folder… → Select a folder for the project
Updating workspace settings
From the official page of VS Code:
A Visual Studio Code "workspace" is the collection of one or more folders that are opened in a VS Code window (instance). In most cases, you will have a single folder opened as the workspace but, depending on your development workflow, you can include more than one folder, using an advanced configuration called Multi-root workspaces.
Before you start working on your project you need to set up your workspace. Two important options that you need to set are
- End of Line character
- Type of configuration
End of Line Character
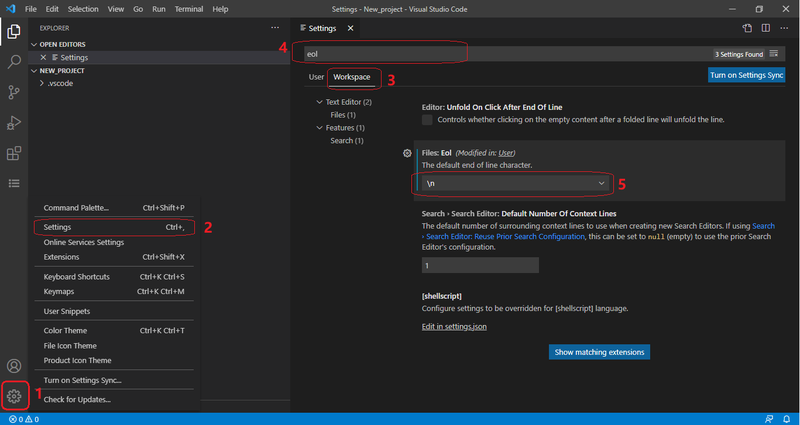
To select the end of line character:
- Click the Manage icon in the Activity bar
- Click Settings in the popup menu
- Select Workspace in the Settings tab
- Type “eol” in the search bar
- Select “\n” (LF) in the Files: EOL drop-down list
After changing EOL the .vscode directory with settings.json will be created in your project folder.
Type of configuration
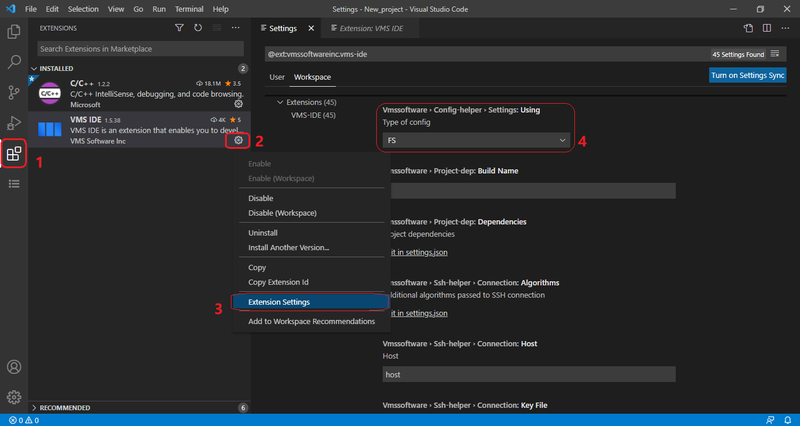
To select the type of configuration:
- Select Extensions view in the Activity bar
- Right-click the Gear icon of the VMS IDE extension
- Click the Extension Settings
- Select the Using Type item of the config from the drop-down list. We recommend using FS (default value)
All project, ssh, and other settings will be saved in JSON files in the .vscode directory of the project folder.
Updating project settings
Create a project configuration file
You need to create a file with project configuration and specify your project settings in it:
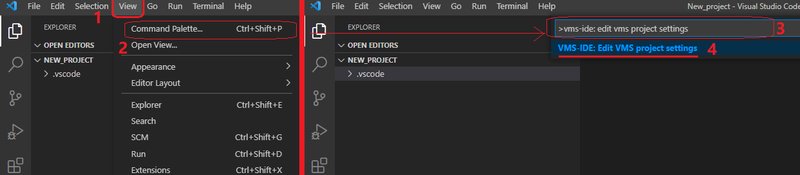
- Click the View menu option
- Select Command Palette… option from the View menu
- Type “>VMS-IDE: edit VMS project settings” in the Command Palette bar
- Select the “VMS-IDE: edit VMS project settings” command from the drop-down list
The editor opens vmssoftware.synchronizer-settings.json
- Specify your project settings (see info about parameters and values below).
- Save file: press <Ctrl>+<S> or select File → Save
The vmssoftware.synchronizer-settings.json file will be saved in the .vscode directory in the root of the project folder.
Customize project configuration
After the file is created you need to customize it specifying the parameters. The structure of the vmssoftware.synchronizer-settings.json file consists of 3 sections:
- Project - general project settings
- Synchronize - synchronizer specific settings
- Builds- build configurations for the project
(!) Follow the links to view all the options for each section.
Generally, in the project section you need to:
- Set the
rootdirectory. For example, if the project is located in WORK:[USER.DEMOS.SIMPLE] and the home directory is WORK:[USER], set the parameter value to demos/simple or /work/user/demos/simple - Select the
projectTypethat you need - Specify the
projectName. WARN: Do not use spaces or special characters in theprojectName - Check
builders. These files will be synchronized. - Check
headers. These files will be synchronized and included in the auto-generated MMS file as header files. Changing any of them will result in a full project rebuild. - Check
source. These files will be synchronized and included in the auto-generated MMS file as source files. - Check
resource. These files will be synchronized but not included in the auto-generated MMS file. - Adjust the
excludefield value to list the files similar to the described above but not to be synchronized and compiled. - Check
listing. These files will be downloaded after building the project. Files "*.lis,*.map" are required for the debugger. - If the project depends on already installed libraries, specify them in the
addLibrariesandaddIncludes
Glob syntax:
* to match one or more characters in a path segment
? to match one character in a path segment
** to match any number of path segments, including none
{} to group conditions (for example {**/*.html,**/*.txt} matches all HTML and text files)
[] to declare a range of characters to match (example.[0-9] to match on example.0, example.1, …)
Generally, in the synchronize section you need to:
Select the downloadNewFiles value - strategy for downloading remote files that are newer than local copies.
- If you have the full project on OpenVMS and want to download it to your local machine, set
downloadNewFilesto overwrite. - If you have the full project on your local machine and use OpenVMS only for compiling and debugging, set
downloadNewFilesto skip. - If the project on OpenVMS can be changed outside and may be newer than the local copy, set
downloadNewFilesto edit.
Generally, in the build section you need to:
- Specify label - unique name of the build configuration. Note: the label is also used as the name of the output folder.
- Add a description - description of the build configuration
By default, there are two build configurations:
- DEBUG, which is necessary for debugging
- RELEASE, which produces binaries for your project deployment.
For custom build configurations for your project see here. Example of vmssoftware.synchronizer-settings.json
{
"project": {
"break": "C",
"builders": "*.{mms,com,opt}",
"exclude": "**/{.vscode}/**,**/.git/**,*gitignore*",
"headers": "*.h",
"listing": "*.lis,*.map",
"outdir": "out",
"projectName": "NEW_PROJECT",
"projectType": "executable",
"resource": "**/resource/**",
"root": "/USR_DISK/TEST_USER/NEW_PROJECT",
"source": "*.{cpp,c,cld,msg}",
"addCompQual": "",
"addCompDef": "",
"addLibraries": "",
"addIncludes": ""
},
"synchronize": {
"downloadNewFiles": "edit",
"keepAlive": false,
"preferZip": false,
"forceLocalTime": true,
"purge": false,
"setTimeAttempts": 3
},
"builds": {
"configurations": [
{
"label": "DEBUG",
"description": "NEW_PROJECT 1.0.1 debug,
"command": "",
"parameter": "DEBUG"
},
{
"label": "RELEASE",
"description": "NEW_PROJECT 1.0.1 release",
"command": "",
"parameter": "RELEASE"
}
]
}
}
Updating SSH settings
Create SSH settings configuration file
For syncing source code files, building, running, and debugging project you need to create a file with SSH configuration and specify your SSH settings in it:
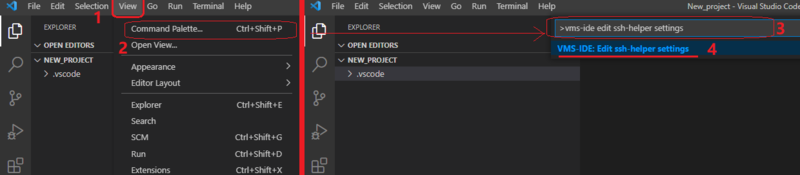
- Select the View menu option
- Select Command Palette… option from the View menu
- Type “>VMS-IDE: edit VMS ssh-helper settings” in the Command Palette bar
- Select the “VMS-IDE: edit VMS ssh-helper settings” command from the drop-down list
The editor opens vmssoftware.ssh-helper-settings.json
- Specify your SSH settings (see info about parameters and values below).
- Save file: press <Ctrl>+<S> or select File → Save
The vmssoftware.ssh-helper-settings.json file will be saved in the .vscode directory in the root of the project folder.
Customize SSH settings configuration file
After the file is created you need to specify the required parameters. The vmssoftware.ssh-helper-settings.json file consists of 4 sections:
- connection - the current connection details
- host-collection - a list of connections required for the project
- timeouts - SSH connection timeouts
- terminal - command to start the shell in the VS Code integrated terminal
Generally, in the connection section you need to specify:
Required
- Specify
host- IP-address or name of an OpenVMS machine or the label of a predefined connection from the host collection section. In the latter case, all other fields in the connection section are ignored. username- User account that will be used for the SSH connection.
Optional
password- User password that will be used for the SSH connection. If it is omitted, a password input box will be shown on a connection attempt.keyFile- Path to the SSH private key file. For details on how to configure a connection using an SSH key, see SSH public key authentication on OpenVMS
If you need to connect to different servers when working on your project specify their settings in the host collection section. Typically the settings for every host are:
- label - label for the current host's settings. It can be used as a host in the connection section
- host
- password or key
- port
- username
To use one of the connections from the host collection section, copy the label value and paste it in angle brackets (<label>) to the host field in the connection section.
Example of vmssoftware.ssh-helper-settings.json for a project with 2 hosts.
{
"connection": {
"host": "<Boston keys>"
},
"host-collection": {
"hosts": [
{
"host": "104.207.199.181",
"keyFile": "h:/.ssh/sv01",
"port": 22,
"username": "vorfolomeev",
"label": "Boston keys"
},
{
"host": "104.207.199.181",
"keyFile": "",
"port": 22,
"username": "vorfolomeev",
"label": "Boston pass"
}
]
},
"timeouts": {
"cmdTimeout": 0,
"feedbackTimeout": 0,
"welcomeTimeout": 0
},
"terminal": {
"command": ""
}
}
Follow the link to view all options for each section.
Working on a project
Synchronizing
Synchronizing allows you to transfer your project files between remote and local machines. Synchronization lists files on a VMS machine and your local machine starting from the root directory. The files are identified by the source, headers, builders, resource masks. Files matching masks listed in the exclude section are ignored.
To download files from a remote machine to the local
- Set the value of downloadNewFiles option (see Updating project settings for details) in the vmssoftware.synchronizer-settings.json file
- Invoke “Command Palette”: press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<P>
- Type “>vms-ide: synchronize project files with VMS” in the Command Palette bar
- Select the “vms-ide synchronize project files with VMS” command from the drop-down list
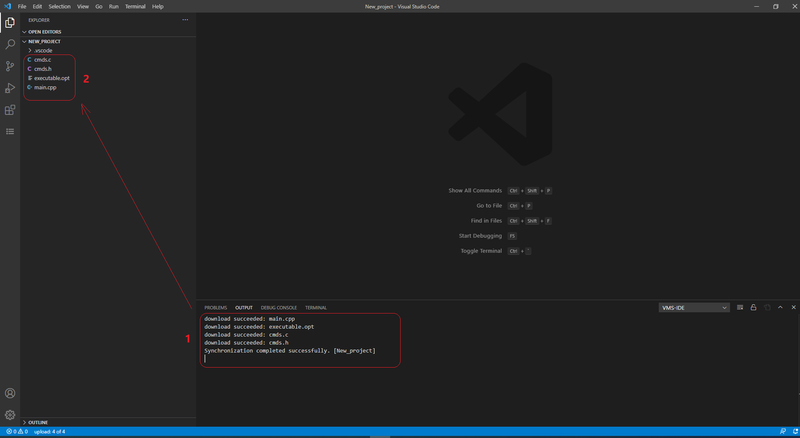
If you specified “downloadNewFiles:overwrite” files from a remote machine will be downloaded. Local files with the same names will be overwritten. Info about the synchronization process is shown in the panel. Downloaded files can be verified in the Explorer view of the Activity bar.
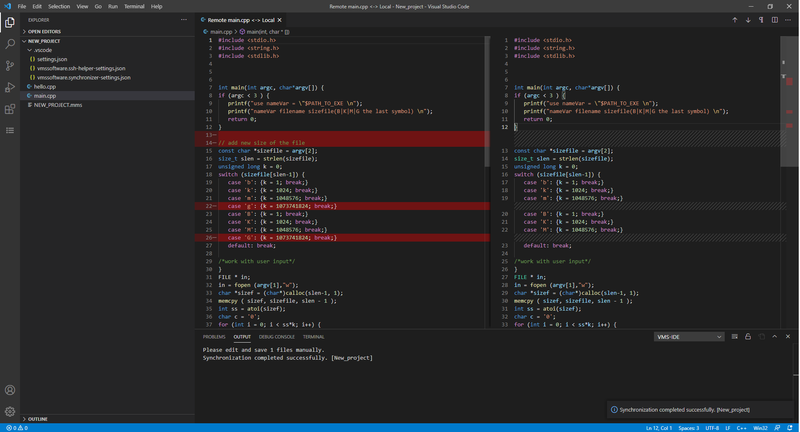
If you specified “downloadNewFiles:edit” files from a remote machine will be downloaded into memory and the edit-merge window will be opened to let you decide what changes to save. Make necessary changes on the local side and save files using keyboard shortcut<Ctrl>+<S>.
To upload files from the local machine to a remote one
If you have project files only on your local machine and want to upload them to a remote machine:
- Invoke “Command Palette”: press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<P>
- Type “>vms-ide: Upload all” in the Command Palette bar
- Select the “vms-ide: Upload all” command from the drop-down list
Files from your local machine will be upload to a remote one. Info about the synchronization process will be shown in the panel. Uploaded files can be verified on the remote side:
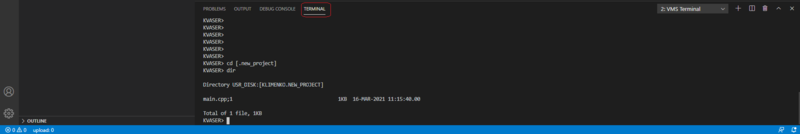
- Invoke “Command Palette”: press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<P>
- Type “>vms-ide: Terminal” in the Command Palette bar
- Select the “vms-ide: Terminal” command from the drop-down list
- Move to the root project directory in the command prompt of the Terminal tab in the panel.
- Use the “dir” command to show uploaded files.
If you have files on both sides use the vms-ide: synchronize project files with VMS command (see the description below).
Managing dependencies
From the official documentation of VS Code:
When building a solution that contains multiple projects, it can be necessary to build certain projects first, to generate code used by other projects. When a project consumes executable code generated by another project, the project that generates the code is referred to as a project dependency of the project that consumes the code.
Such dependency relationships can be defined in the Project Dependencies dialog box.
Project types:
- executable - source files will be built and linked in the executable image
- library - object library (OLB) will be created
- shareable - extension will create a shareable image
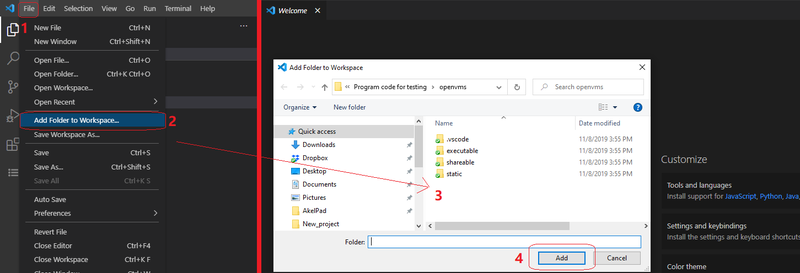
Adding all projects to the workspace:
- Click the File menu option
- Click Add folder to workspace…
- Select the folder of the project in the dialog window
- Click the Add button
The selected folder is shown in the Explorer view.
Saving the workspace
For quick access to the workspace with multiple projects save the workspace as a file:
- Select File menu option
- Select Save workspace as…
- Type the file name
- Click the Save button
After the workspace is saved you can access it by File → Open workspace…
Managing dependencies
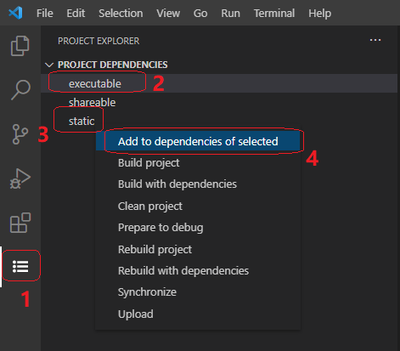
- Select the Project Explorer view in the Activity bar
- Select the main project in the Project Explorer panel
- Right-click the project that you want to add as a dependency to the main project
- Click Add to dependencies of selected from the menu
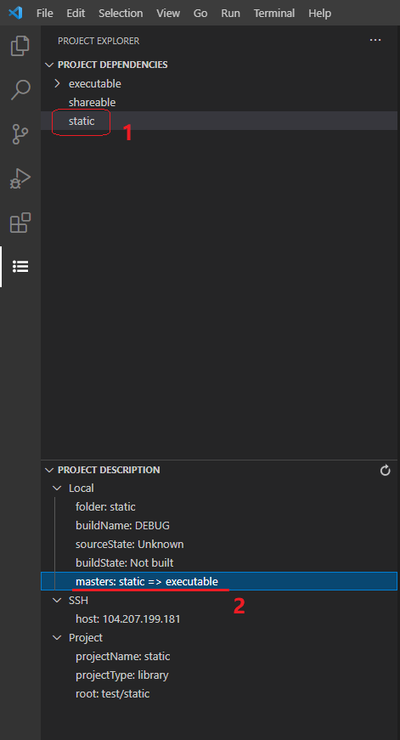
To verify the created dependency:
- Select the project added to the dependencies in the Project Explorer panel
- The Project description section will contain the master parameter showing the dependency
Building a project
To build a project you need to:
- Create an MMS file
- Upload your project files to a remote machine
- Build on VMS
Creating an MMS file
- Select the Project Explorer in the Activity bar
- Select the project
- Invoke “Command Palette”: press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<P>
- Type “>vms-ide create/update MMS” in the Command Palette bar
- Select the “vms-ide create/update MMS” command from the drop-down list
Info about the MMS file will be shown in the Output tab of the panel. Created MMS file will be located at the root of the project.
If you work on a project with dependencies, create MMS files for every project.
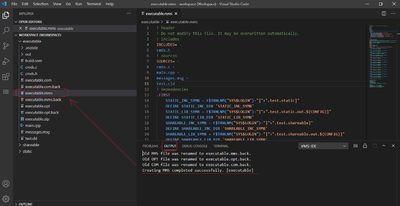
Upload your project files to a remote machine
- Select the Project Explorer in the Activity bar
- Select the project
- Invoke “Command Palette”: press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<P>
- Type “>vms-ide: Upload all” in the Command Palette bar
- Select the “vms-ide: Upload all” command from the drop-down list
Building on VMS
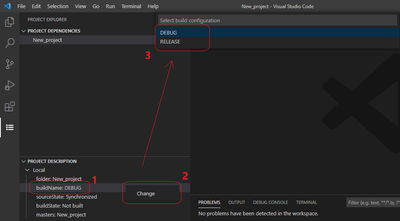
- Select the Project Explorer in the Activity bar
- Select the project
- Right-click the buildName in the project description of the Project Explorer, then select Change → Select build configuration
- Invoke “Command Palette”: press <Ctrl>+<Shift>+<P>
- Type “>vms-ide: build project” in the Command Palette bar
- Select the “vms-ide: build project” command from the drop-down list
The project will be built. Info about the build process will be shown in the Output tab.